Anhui Feichun Special Cable Co.,Ltd Email: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
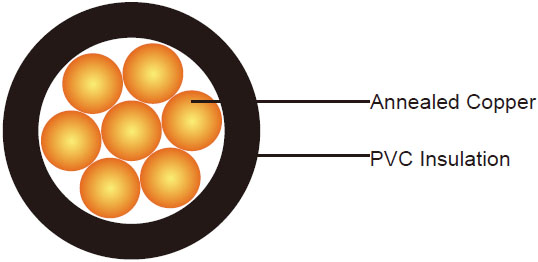
450/750V PVC Insulated, Non-sheathed Power Cables (Single Core 90°C)
Understanding 450/750V PVC-Insulated Non-Sheathed Power Cables for Modern Application
450/750V PVC Insulated, Non-sheathed Power Cables (Single Core 90°C)
FGD100 07V2-U/R/K (CU/PVC 450/750V Class 1/2/5)
BS Code: 6491XHR
HAR Code: H07V2-U, H07V2-R, H07V2-K
Application
This cables are mainly used in power stations, mass transit underground passenger systems, airports, petrochemical plants, hotels, hospitals, and high-rise buildings.
Standards
Basic design to to BS EN 50525-2-31(formerly BS 6004:2000)
Fire Performance
Flame Retardance (Single Vertical Wire Test) | EN 60332-1-2 |
Voltage Rating
450/750V
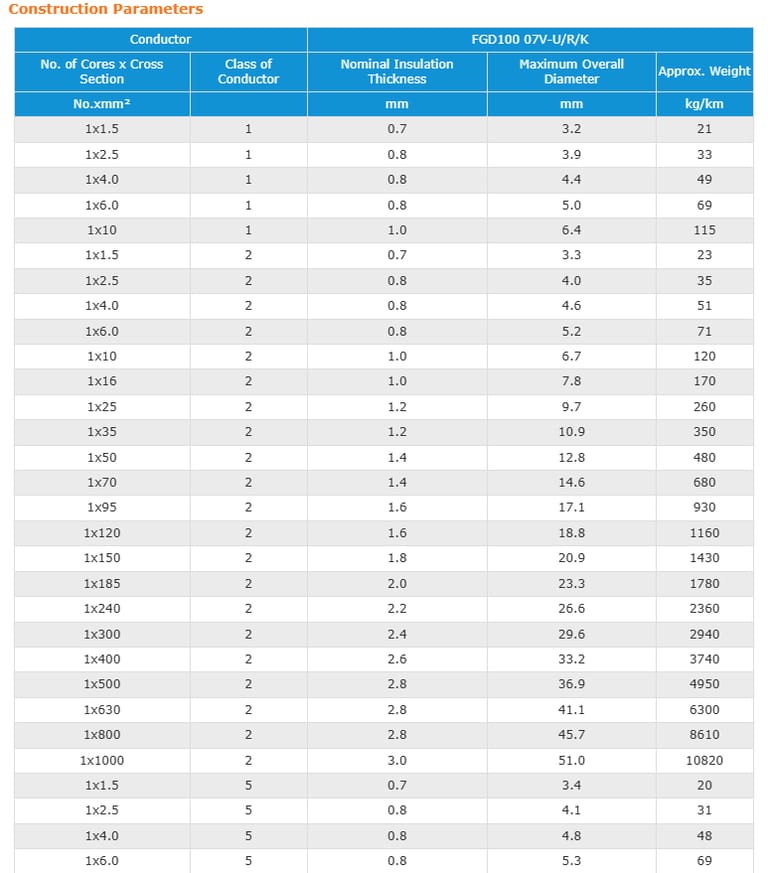
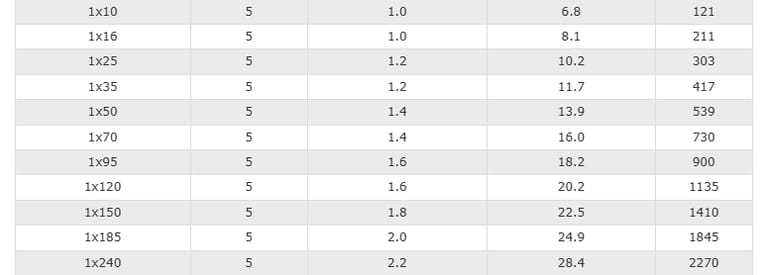
Cable Construction
Conductor | H05V-U: Class 1 solid copper conductor to BS EN 60228. |
| H05V-R: Class 2 stranded copper conductor to BS EN 60228. |
| H05V-K: Class 5 stranded copper conductor to BS EN 60228. |
Insulation | PVC Type TI 3 according to BS EN 50363-3 |
Colour Code
Black, Blue, Brown, Grey, Orange, Pink, Red, Turquoise, Violet, White, Green and Yellow.
Physical and Thermal Properties
Maximum temperature range during operation (PVC) | 90°C |
Maximum short circuit temperature (5 Seconds) | 160°C |
Minimum bending radius | Up to 8mm^2: 4 x overall diameter |
| 8mm^2 to 12mm^2: 5 x overall diameter |
| Above 12mm^2: 6 x overall diameter |
ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES
Conductor Operating Temperature | 90°C |
Ambient Temperature | 30°C |
Current-Carrying Capacities (Amp) according to BS 7671:2008 table 4E1A
Conductor cross- sectional area | Reference Method A (enclosed in conduit in thermally insulating wall etc) | Reference Method B (enclosed in conduit on a wall or in trunking etc) | Reference Method C (clipped direct) | Reference Method F (in free air or on a perforated cable tray, horizontal or vertical etc) Touching | Reference Method G (in free air) Spaced by one cable diameter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2 cables, single- phase a.c. or d.c. | 3 or 4 cables, three -phase a.c. | 2 cables, single- phase a.c. or d.c | 3 or 4 cables, three- phase a.c. | 2 cables, single- phase a.c. or d.c. flat and touching | 3 or 4 cables, three- phase a.c. flat and touching or trefoil | 2 cables, single- phase a.c. or d.c. flat | 3 cables, three- phasea.c. flat | 3cables, three- phase a.c. trefoil | 2 cables, single- phase a.c. or d.c. or 3 cables three- phase a.c. flat | ||
Horizontal | Vertical | ||||||||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
mm² | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
1.5 | 19 | 17 | 23 | 20 | 25 | 23 | - | - | - | - | - |
2.5 | 26 | 23 | 31 | 28 | 34 | 31 | - | - | - | - | - |
4.0 | 35 | 31 | 42 | 37 | 46 | 41 | - | - | - | - | - |
6.0 | 45 | 40 | 54 | 48 | 59 | 54 | - | - | - | - | - |
10 | 61 | 54 | 75 | 66 | 81 | 74 | - | - | - | - | - |
16 | 81 | 73 | 100 | 88 | 109 | 99 | - | - | - | - | - |
25 | 106 | 95 | 133 | 117 | 143 | 130 | 161 | 141 | 135 | 182 | 161 |
35 | 131 | 117 | 164 | 144 | 176 | 161 | 200 | 176 | 169 | 226 | 201 |
50 | 158 | 141 | 198 | 175 | 228 | 209 | 242 | 216 | 207 | 275 | 246 |
70 | 200 | 179 | 253 | 222 | 293 | 268 | 310 | 279 | 268 | 353 | 318 |
95 | 241 | 216 | 306 | 269 | 355 | 326 | 377 | 342 | 328 | 430 | 389 |
120 | 278 | 249 | 354 | 312 | 413 | 379 | 437 | 400 | 383 | 500 | 454 |
150 | 318 | 285 | 393 | 342 | 476 | 436 | 504 | 464 | 444 | 577 | 527 |
185 | 362 | 324 | 449 | 384 | 545 | 500 | 575 | 533 | 510 | 661 | 605 |
240 | 424 | 380 | 528 | 450 | 644 | 590 | 679 | 634 | 607 | 781 | 719 |
300 | 486 | 435 | 603 | 514 | 743 | 681 | 783 | 736 | 703 | 902 | 833 |
400 | - | - | 683 | 584 | 868 | 793 | 940 | 868 | 823 | 1085 | 1008 |
500 | - | - | 783 | 666 | 990 | 904 | 1083 | 998 | 946 | 1253 | 1169 |
630 | - | - | 900 | 764 | 113 | 1033 | 1254 | 1151 | 1088 | 1454 | 1362 |
800 | - | - | - | - | 1288 | 1179 | 1358 | 1275 | 1214 | 1581 | 1485 |
1000 | - | - | - | - | 1443 | 1323 | 1520 | 1436 | 1349 | 1775 | 1671 |
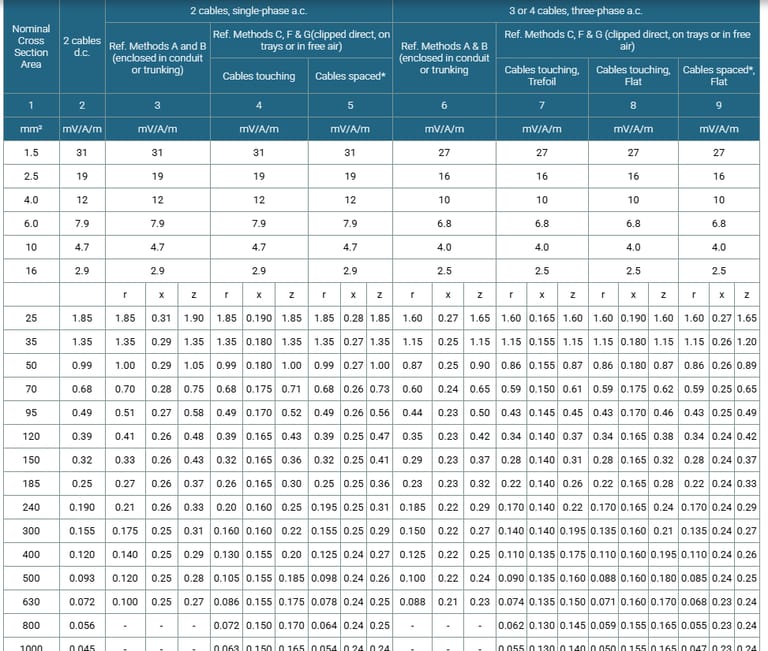
Voltage Drop (Per Amp Per Meter) according to BS 7671:2008 table 4E1B
Introduction to 450/750V PVC-Insulated Power Cables
In the intricate world of electrical infrastructure, 450/750V PVC-insulated, non-sheathed power cables (single core, 90°C) stand out as a cornerstone for reliable power distribution. These cables, designed to handle significant electrical loads while maintaining safety and efficiency, are critical in environments ranging from power stations to high-rise buildings. Known by standards such as BS EN 50525-2-31 and HAR codes (H07V2-U, H07V2-R, H07V2-K), these cables are engineered for durability and performance under demanding conditions.
Standards and Compliance
The 450/750V PVC-insulated cables adhere to international standards to ensure safety and reliability:
BS EN 50525-2-31: Replaces BS 6004:2000, outlining design and performance requirements.
BS EN 60332-1-2: Ensures flame retardance through the single vertical wire test, critical for fire safety in confined spaces.
BS EN 60228: Specifies conductor classes for consistent electrical performance.
HAR Codes: H07V2-U, H07V2-R, and H07V2-K align with European harmonized standards for cross-border compatibility.
Applications and Usage Scenarios
The versatility of 450/750V PVC-insulated cables makes them indispensable in various settings:
Power Stations: Used for internal wiring due to their high current-carrying capacity and heat resistance.
Mass Transit Systems: Employed in underground passenger systems for reliable power distribution in confined, high-traffic areas.
Airports: Support critical infrastructure, such as lighting and control systems, where flame retardance is essential.
Petrochemical Plants: Withstand harsh chemical environments while maintaining electrical integrity.
Hotels and Hospitals: Ensure safe and reliable power for lighting, HVAC, and medical equipment.
High-Rise Buildings: Facilitate vertical power distribution with minimal voltage drop.
Their non-sheathed design makes them ideal for installations within conduits or trunking, where additional protection is provided by the installation environment.
The 450/750V PVC-insulated, non-sheathed power cables (single core, 90°C) are a vital component of modern electrical systems, offering reliability, safety, and versatility. Their adherence to stringent standards like BS EN 50525-2-31 and BS EN 60332-1-2 ensures performance in demanding applications, from power stations to renewable energy projects. In South Africa, these cables address pressing challenges like fire safety, urbanization, and energy access, as demonstrated in case studies from Khayelitsha, Gauteng, and Johannesburg.

Email Address: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
© 2025. All rights reserved.


One-click to Quickly Contact
Products
Contact
Company
Location:
Building A Private Science and Technology Park, Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone, Anhui Province, China
Heat Resistant Cable
WhatsApp: +86 17333223430
