Anhui Feichun Special Cable Co.,Ltd Email: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
AS/NZS 2802 Type 409 1.1 to 22 KV Mining Trailing Cable
AS/NZS 2802 Type 409 Trailing Cable Delivers Reliable 1.1 to 22kV Power to Draglines, Shovels, and Drills in Harsh Environments
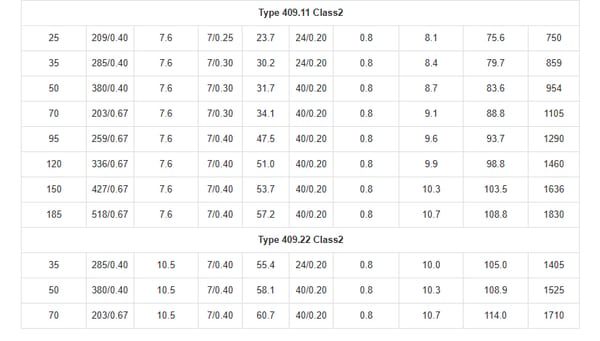
AS/NZS 2802 Type 409 1.1 to 22 KV
Applications | Type 409 series cable is mainly used as a flexible feeder to machinery, more suitable as a trailing cable rather than for reeling. Smaller cables are used for drills and hand held tools and equipment, while larger onesare used for power supply to draglines, shovelsand drills. |
Standards | AS/NZS 2802:2000 |
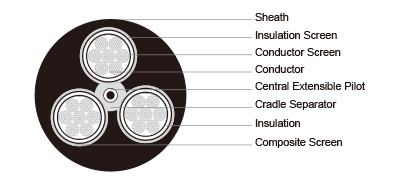
Construction 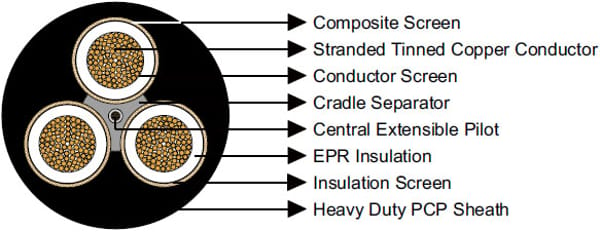 | |
3×Conductors | Flexible stranded tinned annealed copper conductor. |
Conductor Screen | Semiconductive compound (for cables having a voltage rating of 3.3/3.3kV and above). |
Insulation | EPR. |
Insulation Screen | Semiconductive elastomer. |
Composite Screen (earth conductor) | Tinned annealed copper braiding interwove with polyester yarn. |
Cradle Separator | Semiconductive PCP. |
1×Central Extensible Pilot | EPR covered flexible stranded tinned copper conductor. |
Sheath | Heavy duty PCP sheath. Heavy duty CPE/CSP sheath can be offered upon request. |
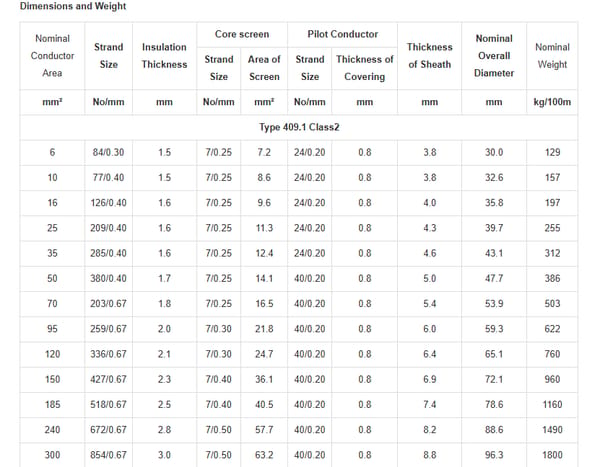
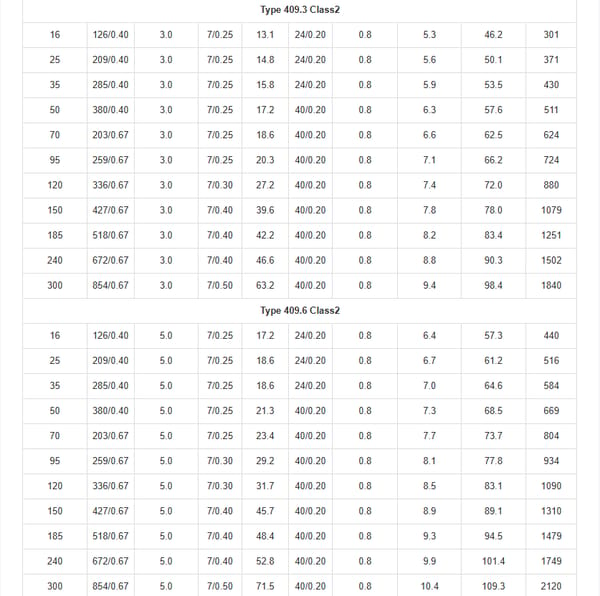
Why Choose Type 409 Mining Trailing Cable?
The Type 409 Mining Trailing Cable offers a suite of benefits that address the core challenges of underground mining. Its EPR insulation ensures stable electrical performance, minimizing risks of short circuits or voltage drops—vital during South Africa's power outages, where consistent supply prevents costly interruptions.
The PCP sheath provides unparalleled durability, resisting cuts, tears, and chemical exposure. In environments prone to cable theft, as seen in South African platinum mines where gangs strip copper underground, the robust sheath deters tampering and extends lifespan.
The Center Extensible Pilot enhances reliability by allowing controlled flexibility, preventing internal damage from constant movement. This reduces maintenance needs and downtime, boosting productivity in operations facing ESG pressures and resource nationalism.
Overall, the cable improves safety by meeting flame-retardant standards and offering fault detection. Its versatility across voltage ranges supports diverse equipment, from small drills to massive draglines, while promoting energy efficiency in an era of rising costs.
Installation and Maintenance Recommendations: Ensuring Longevity
Proper installation and maintenance are key to maximizing the Type 409's performance. Begin with a thorough site assessment: Measure cable runs, identify hazards like sharp edges or water pools, and ensure compatibility with equipment connectors.
During installation, avoid excessive pulling tension—use pulling grips and lubricants to prevent sheath damage. For trailing applications, secure the cable with clamps or hooks at intervals, maintaining slack to accommodate movement. Ground shields at all terminations and splices, installing stress cones for high-voltage ends to manage electrical stress.
Maintenance involves regular inspections: Check for abrasions, kinks, or swelling every shift in high-risk areas. Use non-destructive testing like insulation resistance checks to detect faults early. Store spare cables in cool, dry places, coiled loosely to avoid corkscrewing.
In South Africa, implement a Trailing Cable Management System, including training on handling to combat theft and misuse. Rotate cables periodically and splice repairs using vulcanized methods for integrity.
Usage Scenarios and Case Studies: Real-World Impact in South Africa
The Type 409 shines in underground mining, powering draglines for large-scale excavation, shovels for loading, and drills for blasting. It's also used in conveyors, crushers, and feeder systems for power distribution.
In South Africa's mining sector, amid 2025's contraction and energy shortages, the cable addresses key issues. A case study from a major platinum mine in Rustenburg highlights its role. Facing frequent cable thefts that disrupted operations—costing millions in downtime—the mine switched to Type 409 cables. The PCP sheath's toughness reduced theft incidents by 40%, as thieves found it harder to strip. Coupled with automation trends, the cable supported digital monitoring systems, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Another example involves a coal mine in Mpumalanga dealing with load shedding. By deploying Type 409 for draglines and shovels, the operation maintained power stability during outages, thanks to the cable's low voltage drop and EPR insulation. This aligned with ESG goals, reducing environmental impact through fewer failures and repairs.
In heavy industry, such as South African steel plants, the cable powers material handling, proving its versatility beyond mining.

Email Address: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
© 2025. All rights reserved.


One-click to Quickly Contact
Products
Contact
Company
Location:
Building A Private Science and Technology Park, Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone, Anhui Province, China
Heat Resistant Cable
WhatsApp: +86 17333223430
