Anhui Feichun Special Cable Co.,Ltd Email: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
H05V2V2-F / H05V2V2H2-F
Application and Description
These cables are suitable for domestic premises, kitchen, office for light service or light portable apparatuses. With their special insulation and sheath compounds these cables are adapt for apparatus in kitchen and heating and for use in zones with high temperature (like lighting system apparatuses) without contact with warm parts and radiations. Unsuitable for outdoor use, in industrial and agricultural buildings or non-domestic portable tools. The maximum conductor temperature in normal use: 90°C.While high
temperature use, skin contact must be avoided
Standard and Approval
HD 21.12; HD 308 S2, DIN VDE 0281 part 1, part 12, DIN VDE 0293 part 308, DIN VDE 0295
CEI 20-20/12, CEI 20-35 (EN60332-1) / CEI 20-37 (EN50267), CENELEC HD 21.12 S1 /EN50265-2-1
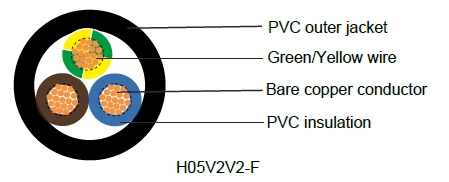
Cable Construction
- Bare copper fine wire conductor
- Stranded to DIN VDE 0295 cl. 5, IEC 60228 cl. 5 and HD 383
- PVC core insulation T13 to VDE-0281 Part 1
- Green-yellow grounding (3 conductors and above)
- Color coded to VDE-0293-308
- PVC outer jacket TM3
Technical Characteristics
- Working voltage: 300/500 volts
- Test voltage: 2000 volts
- Flexing bending radius: 15 x Ø
- Static bending radius: 4 x Ø
- Flexing temperature: +5º C to +90º C
- Static temperature: -40º C to +90º C
- Short circuit temperature: +160º C
- Flame retardant: IEC 60332.1
- Insulation resistance: 20 MΩ x km
Cable Parameter
AWG | NO. OF CORES X NOMINAL CROSS SECTIONAL AREA # X MM² | NOMINAL THICKNESS OF INSULATION MM | NOMINAL THICKNESS OF SHEATH MM | NOMINAL OVERALL DIAMETER MM | NOMINAL COPPER WEIGHT KG/KM | NOMINAL WEIGHT KG/KM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
H05V2V2-F | ||||||
18(24/32) | 0.6 | 0.8 | 6.2 | 14.4 | 54.2 | |
18(24/32) | 0.6 | 0.8 | 6.6 | 21.6 | 65 | |
18(24/32) | 0.6 | 0.8 | 7.1 | 29 | 77.7 | |
18(24/32) | 0.6 | 0.9 | 8 | 36 | 97.3 | |
17(32/32) | 0.6 | 0.8 | 6.4 | 19 | 60.5 | |
17(32/32) | 0.6 | 0.8 | 6.8 | 29 | 73.1 | |
17(32/32) | 0.6 | 0.9 | 7.6 | 38 | 93 | |
17(32/32) | 0.6 | 0.9 | 8.3 | 48 | 111.7 | |
16(30/30) | 0.7 | 0.8 | 7.4 | 29 | 82.3 | |
16(30/30) | 0.7 | 0.9 | 8.1 | 43 | 104.4 | |
16(30/30) | 0.7 | 1.0 | 9 | 58 | 131.7 | |
16(30/30) | 0.7 | 1.1 | 10 | 72 | 163.1 | |
14(30/50) | 0.8 | 1.0 | 9.2 | 48 | 129.1 | |
14(30/50) | 0.8 | 1.1 | 10 | 72 | 163 | |
14(30/50) | 0.8 | 1.1 | 10.9 | 96 | 199.6 | |
14(30/50) | 0.8 | 1.2 | 12.4 | 120 | 245.4 | |
12(56/28) | 0.8 | 1.2 | 11.3 | 115 | 224 | |
12(56/28) | 0.8 | 1.2 | 12.5 | 154 | 295 | |
12(56/28) | 0.8 | 1.4 | 13.7 | 192 | 361 | |
10(84/28) | 0.8 | 1.1 | 13.1 | 181 | 328 | |
10(84/28) | 0.8 | 1.3 | 13.9 | 230 | 490 | |
H05V2V2H2-F | ||||||
18(24/32) | 2 x 0.75 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 4.2 x 6.8 | 14.1 | 48 |
17(32/32) | 2 x 1.00 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 4.4 x 7.2 | 19 | 57 |
Introduction
In the realm of electrical engineering and industrial applications, the choice of cabling plays a pivotal role in ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability. Among the myriad options available, the H05V2V2-F and H05V2V2H2-F harmonized code industrial cables stand out for their specialised design tailored to environments with elevated temperatures. These cables, often referred to as heat-resistant PVC flexible cords, are engineered to withstand conductor temperatures up to 90°C in normal operation, making them ideal for light-duty applications in domestic and commercial settings.
Harmonized cables like these adhere to European standards but find global applicability, including in South Africa, where electrical installations must comply with local regulations such as those from the South African National Standards (SANS). The H05V2V2-F is a round flexible cable, while the H05V2V2H2-F is its flat variant, both featuring PVC insulation and sheathing compounds that enhance thermal resistance without compromising flexibility.
Applications and Description
The H05V2V2-F and H05V2V2H2-F cables are primarily suited for indoor environments where light mechanical stress is anticipated. They excel in domestic premises, kitchens, and offices for connecting light portable apparatuses or fixed installations. Their special insulation and sheath compounds make them adaptable for use in high-temperature zones, such as near lighting systems or kitchen appliances, provided there is no direct contact with hot surfaces or radiations.
Key to their design is the avoidance of skin contact during high-temperature operations, as the outer sheath can become warm. These cables are unsuitable for outdoor applications, industrial or agricultural buildings, or non-domestic portable tools due to their limited resistance to environmental stressors like UV exposure or heavy abrasion. In South African contexts, they might be found in urban households in Johannesburg or office blocks in Cape Town, powering appliances like toasters, kettles, or desk lamps.
From a scientific perspective, the heat resistance stems from the modified PVC formulation, which delays thermal degradation. PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a thermoplastic polymer known for its versatility, but standard variants soften above 70°C. The V2 designation in the cable code indicates enhanced heat resistance, allowing operation at 90°C without significant loss of mechanical properties. This is achieved through additives that improve cross-linking and thermal stability, reducing the risk of insulation breakdown under load.
Standards and Approvals
Compliance with international standards is a hallmark of reliable industrial cables. The H05V2V2-F and H05V2V2H2-F adhere to harmonized directives such as HD 21.12, HD 308 S2, DIN VDE 0281 parts 1 and 12, DIN VDE 0293 part 308, and DIN VDE 0295. Additionally, they meet Italian standards like CEI 20-20/12 and CEI 20-35 (EN60332-1) for flame retardancy, CEI 20-37 (EN50267) for low smoke and halogen emissions, and CENELEC HD 21.12 S1 / EN50265-2-1.
In South Africa, while SANS 1507 governs flexible cords, these harmonized cables align well with global best practices and can be used where European approvals are recognised. The flame-retardant properties ensure they self-extinguish if ignited, a critical feature in fire-prone environments. Scientifically, this is due to the incorporation of flame retardants like antimony trioxide or halogenated compounds in the PVC matrix, which release gases that dilute combustible vapours.
These approvals underscore the cables' safety profile, making them a preferred choice for applications requiring certification for insurance or regulatory compliance.
In-Depth Analysis
Analysing the H05V2V2-F and H05V2V2H2-F from a scientific lens reveals their strengths in thermal management. The PVC's heat resistance is quantified by its vicat softening temperature, often elevated to over 90°C through stabilisers. Advantages include cost-effectiveness—PVC cables are economical compared to silicone or rubber alternatives—lightweight design for easy installation, and good flexibility for bending radii.
However, disadvantages persist: PVC can emit hydrochloric acid when burned, posing environmental risks, and it's less durable in extreme cold or heat beyond ratings compared to rubber cables. In South African industries, where temperatures can exceed 40°C in summer, these cables outperform standard PVC but fall short for heavy-duty mining or petrochemical applications, as noted in manufacturer guidelines.
Comparatively, rubber cables offer superior flexibility and weather resistance but at higher costs. The harmonized code ensures interoperability across borders, beneficial for South Africa's import-dependent market.
Electrically, ampacity depends on cross-section; for instance, a 2.5 mm² core can handle around 25A at 90°C, per derating factors. Thermally, heat dissipation follows Fourier's law, with PVC's low thermal conductivity (0.12-0.25 W/m·K) aiding insulation but requiring ventilation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between H05V2V2-F and H05V2V2H2-F? The former is round, suitable for general flexible routing, while the latter is flat, ideal for space-constrained or surface-mounted installations.
Can these cables be used outdoors in South Africa? No, they are unsuitable for outdoor use due to UV and moisture vulnerability, as per standards.
What is the maximum temperature for these cables? 90°C for continuous operation, with short-circuit tolerance up to 160°C. Avoid skin contact at high temperatures.
Are they flame retardant? Yes, compliant with IEC 60332.1, ensuring self-extinguishment.
How do I select the right cross-section? Based on current load and voltage drop; consult SANS guidelines or use the table above.
Is PVC environmentally friendly? While recyclable, burning releases toxins; opt for low-smoke variants where possible.
Can they be used in industrial settings? Only for light applications; not for heavy machinery or agricultural tools.
The H05V2V2-F and H05V2V2H2-F harmonized code industrial cables represent a balanced solution for heat-resistant, flexible wiring in light applications. Their PVC construction, standards compliance, and technical prowess make them indispensable in South African domestic and office settings. By understanding their parameters and limitations, users can optimise safety and performance. As electrical demands evolve, these cables continue to embody innovation in materials science, ensuring reliable power delivery in a warming world.

Email Address: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
© 2025. All rights reserved.


One-click to Quickly Contact
Products
Contact
Company
Location:
Building A Private Science and Technology Park, Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone, Anhui Province, China
Heat Resistant Cable
WhatsApp: +86 17333223430
