Anhui Feichun Special Cable Co.,Ltd Email: Li.wang@feichuncables.com

PiMF/TiMF 150/250V Mica Tape + XLPE Insulated, LSOH (SHF1) Sheathed, Individual Screened & Armoured Fire Resistant Instrumentation & Control Cables (Multipair/Multitriple)
Application | These cables are used on board of ships in all locations for fixed installations complying with IEC standards 60092-352 in safety circuit, where fire resistance is required. These cables are fire resistant, flame retardant, low smoke & halogen free, suitable for installations on passenger ships, as on other commercial vessels. |
Standards | IEC 60092-350/351/376/359 |
Construction | |
Conductors | Class 2 stranded copper conductor. |
Insulation | Mica tape + XLPE. |
Cabling Element | Pair/Triple. |
Individual Screen | Al/polyester tape. |
Drain Wire | Tinned copper wire. |
Inner Covering | Lapped polyester tape. |
Armour | Copper wire braid. |
Outer Sheath | LSOH (SHF1). SHF2 can be offered upon request. |
Core Identification | Pair: White/blue with printed pair number and core number. |
Mechanical and Thermal Properties | Bending Radius for Fixed Installations: 6×OD |
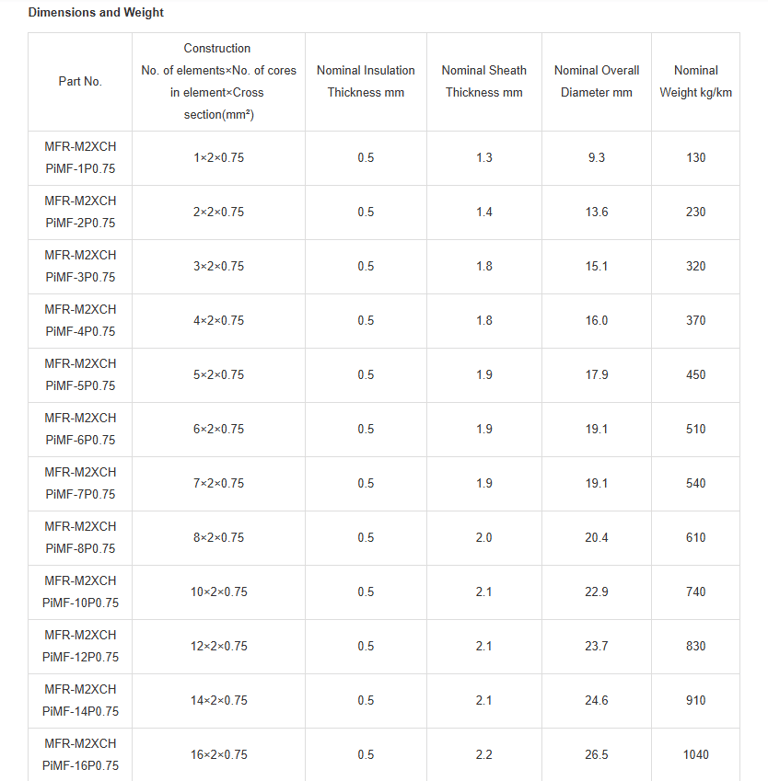
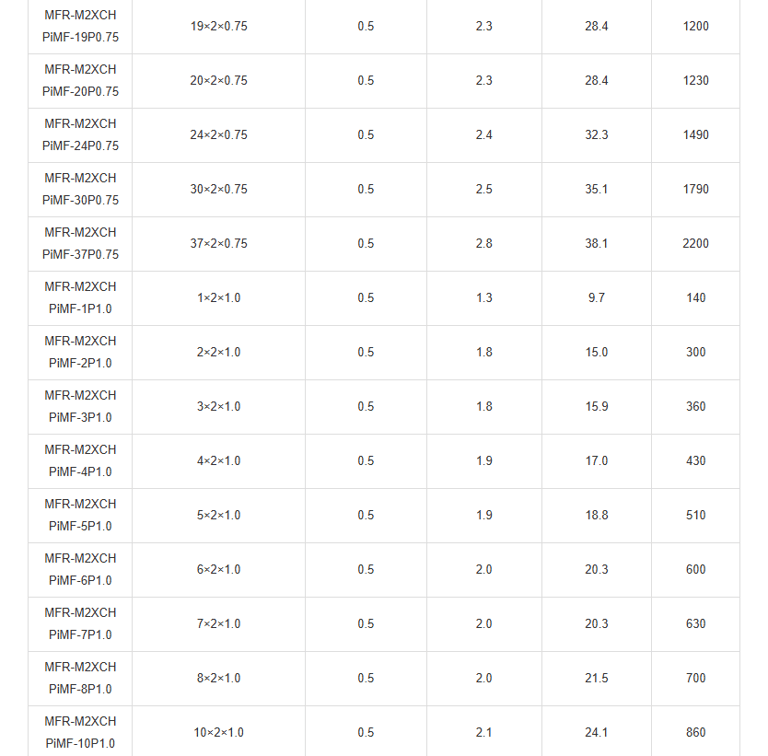
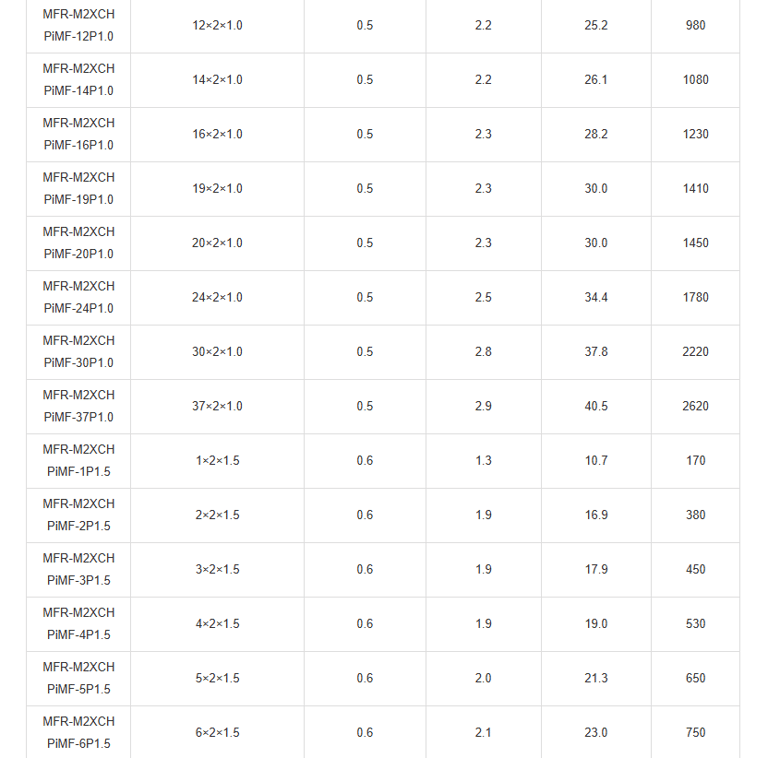
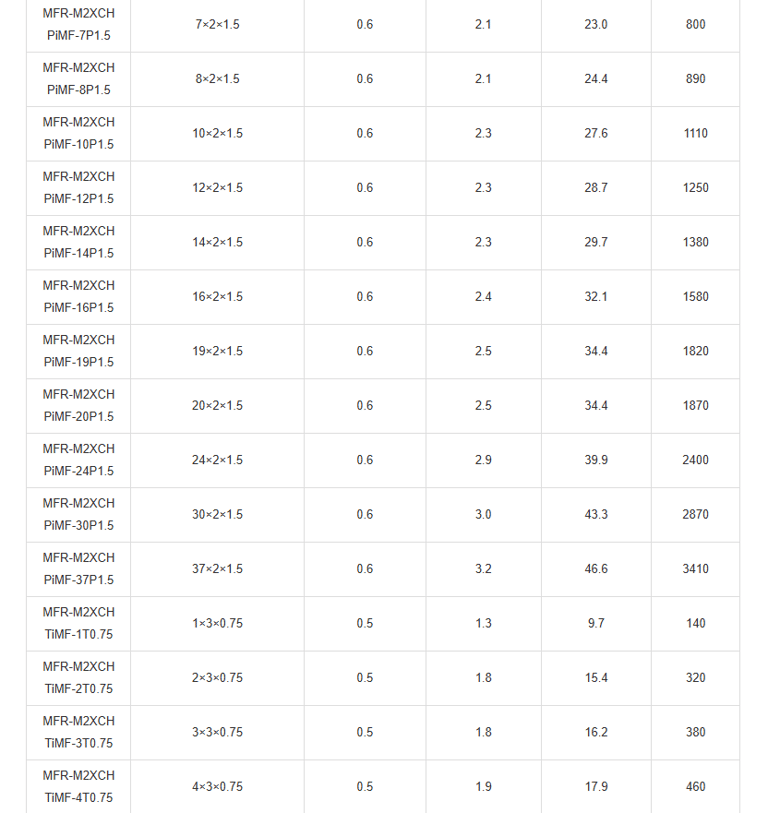
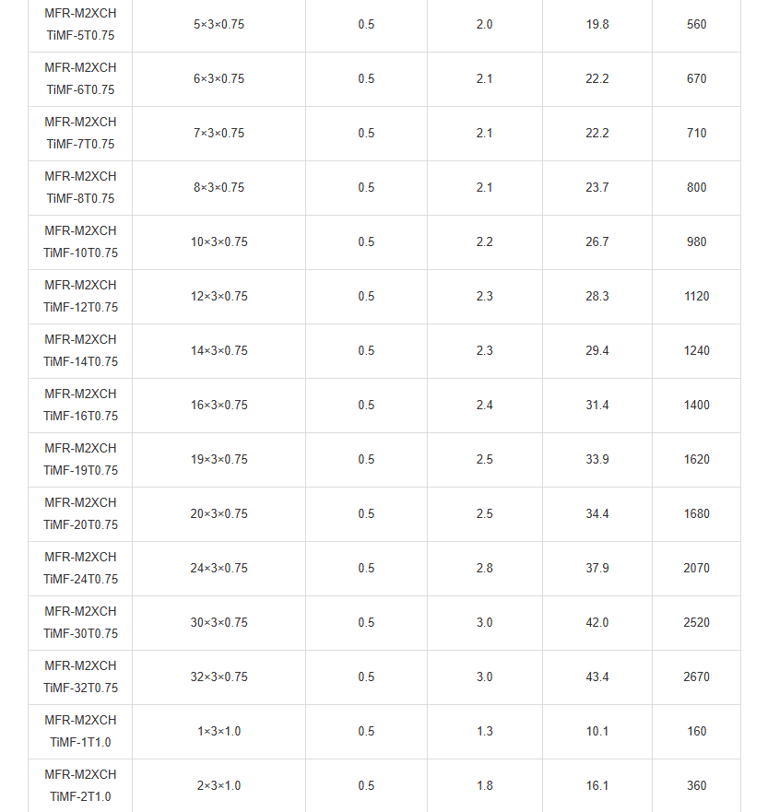
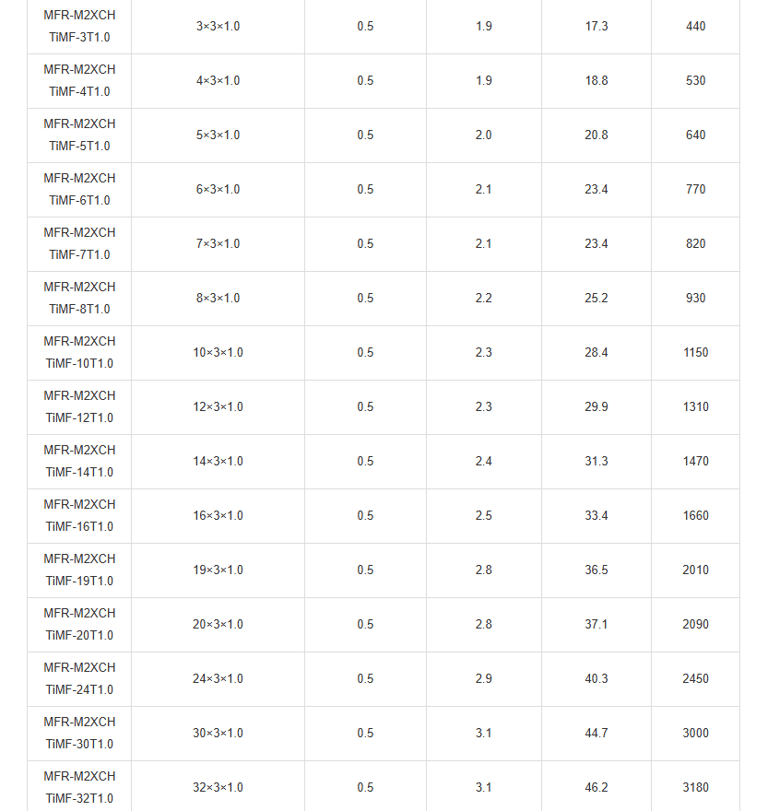
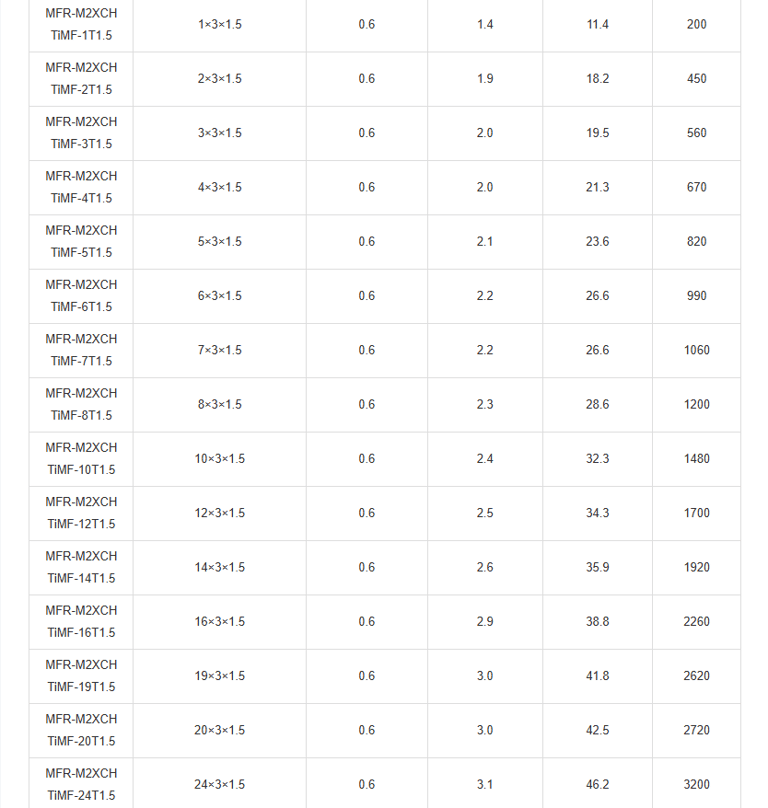
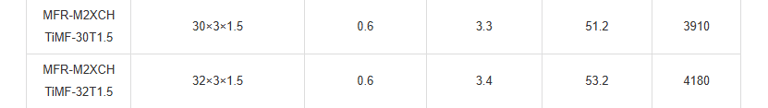
In the vast expanse of the world's oceans, where ships navigate treacherous waters and face unpredictable hazards, safety is paramount. Imagine a passenger liner cruising through stormy seas, or a commercial vessel transporting vital cargo across continents. Beneath the decks, a network of cables pulses with electrical signals, controlling everything from navigation systems to emergency alarms. But what happens when fire breaks out? This is where specialised fire-resistant instrumentation and control cables come into play. Specifically, the PiMF/TiMF 150/250V series – Mica Tape + XLPE Insulated, LSOH (SHF1) Sheathed, Individually Screened & Armoured Fire Resistant Instrumentation & Control Cables (Multipair/Multitriple) – represents a pinnacle of engineering designed for maritime environments. These cables aren't just wires; they're lifelines engineered to withstand extreme conditions, ensuring that critical systems remain operational even amid flames.
Applications:
At the heart of these cables' design is their application in maritime settings. They are primarily used on board ships for fixed installations in safety circuits where fire resistance is non-negotiable. Compliant with IEC 60092-352, these cables ensure that essential systems – like fire alarms, emergency lighting, and control instrumentation – continue functioning during a blaze. This is crucial on passenger ships, where hundreds or thousands of lives depend on swift evacuation, as well as on commercial vessels carrying hazardous materials.
From a safety perspective, fire resistance means these cables can maintain circuit integrity for a specified period under fire conditions. Picture a scenario: a fire erupts in the engine room due to an electrical fault or fuel leak. Ordinary cables might melt or short-circuit, crippling communication and control systems. In contrast, PiMF (Pair in Metal Foil) and TiMF (Triple in Metal Foil) cables keep signals flowing, allowing crew to activate sprinklers, seal bulkheads, or guide passengers to lifeboats. This aligns with global maritime safety protocols, such as those from the International Maritime Organization (IMO), emphasising fire-resistant materials in high-risk zones.
Environmentally, these cables shine with their low smoke and halogen-free properties. In confined ship spaces, smoke from burning cables can be as deadly as flames, reducing visibility and releasing toxic gases. LSOH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) sheathing minimises these risks, making them ideal for passenger vessels where air quality during emergencies is critical. They're suitable for all ship locations, from engine rooms to accommodation areas, highlighting their versatility.
From an operational viewpoint, their use extends beyond fire scenarios. As instrumentation cables, they transmit low-voltage signals (150/250V) for monitoring and control, such as in automation systems for propulsion or cargo handling. Multipair configurations (PiMF) suit paired signal transmission, while multitriple (TiMF) versions handle three-core setups, often for more complex sensor arrays. This adaptability makes them a go-to choice for shipbuilders worldwide, including in South Africa's burgeoning maritime industry, where ports like Durban and Cape Town handle diverse vessels.
Multi-Perspective Analysis: Safety, Environment, Performance, and Beyond
Safety is the cornerstone: fire resistance per IEC 60331-21 could save lives, as seen in historical ship fires like the MS Scandinavian Star disaster in 1990, where cable failures exacerbated chaos. These cables mitigate such risks, maintaining 150/250V circuits for instrumentation.
Environmentally, LSOH sheathing reduces halogen emissions, protecting marine ecosystems during scrapping or incidents. Low smoke aids compliance with SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea) conventions.
Performance reliability stems from screening and armour, curbing EMI in radar-heavy ship environments. Voltage rating suits control signals, not power transmission, ensuring precision.
Installation perspectives: the 6×OD radius eases fitting, but heavy weights (up to 4180kg/km) necessitate winches. Core identification speeds terminations, reducing downtime.
Comparatively, versus non-fire-resistant cables, these add cost but save in insurance and longevity. Future trends might include smart integrations, like fibre optics hybrids, but PiMF/TiMF remain staples.
Economically, in South Africa's ship repair sector (e.g., at Durban Dry Dock), these cables support jobs in specialised manufacturing, bolstering exports.
Cables That Stand the Test of Fire
The PiMF/TiMF series embodies resilience, blending advanced materials with stringent standards to protect lives at sea. From their mica-fortified insulation to armoured exteriors, they offer a comprehensive solution for fire-prone maritime applications. As ships evolve towards automation and sustainability, these cables will undoubtedly play a pivotal role, ensuring safety without compromise. In an era of climate challenges and global trade, investing in such technology isn't just prudent – it's essential.

Email Address: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
© 2025. All rights reserved.


One-click to Quickly Contact
Products
Contact
Company
Location:
Building A Private Science and Technology Park, Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone, Anhui Province, China
Heat Resistant Cable
WhatsApp: +86 17333223430
