Anhui Feichun Special Cable Co.,Ltd Email: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
Single Core Cables to VDE 0276
Dive Into the World of Single Core Cables to VDE 0276
Single Core Cables to VDE 0276
Application
The single core cables are designed for distribution of electrical power with nominal voltage Uo/U ranging from 3.6/6KV to 18/30KV and frequency 50Hz. They are suitable for installation mostly in power supply stations, indoors and in cable ducts, outdoors, underground and in water as well as for installation on cable trays for industries, switchboards and power stations.
Standards
DIN VDE 0276 Part 620-622
HD 620 S1
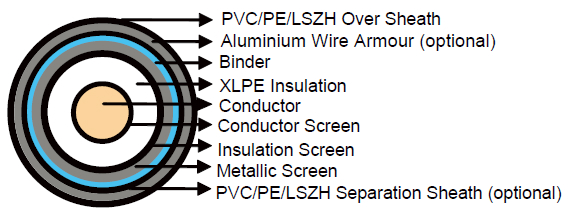
Construction
Conductor : Stranded compacted circular copper or aluminium conductors according to IEC 60228 class 2 / VDE 0276 class 2 / VDE 0295 HD 383. All internal interstices of the conductor are filled with water blocking compound to prevent ingress of water through conductor during storage, handing, installation and operation of the cable.
Conductor Screen : The conductor screen consists of an extruded layer of non metallic, semi-conducting compound firmly bonded to the insulation to exclude all air voids. The screen has a minimum thickness of 0.3mm and the maximum volume resistivity of 500 Ohm-m at 90°C.
Insulation : Insulation is of extruded XLPE compound type 2XI1 according to DIN VDE 0207 part 22 and HD 620.1 with high degree of cross-linking, free from contaminants, air voids and heat resistant by dry cured process.
The nominal insulation wall thickness is shown in table 1.
Table 1. Insulation Thickness
Nom. Cross Section Area of Conductor | Insulation Thickness at Nom. Voltage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3.6/6KV(Um=7.2KV) | 6/10KV(Um=12KV) | 8.7/15KV(Um=17.5KV) | 12/20KV(Um=24KV) | 18/30KV(Um=36KV) | |
mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm |
35 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | - |
50 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 |
70 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 |
95 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 |
120 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 |
150 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 |
185 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 |
240 | 2.6 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 |
300 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 |
400 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 |
Insulation Screen : The insulation screen consists of extruded non metallic, semi-conducting compound extruded over the insulation. The extruded semi-conducting layer shall consist of bonded or cold strippable semi-conducting compound capable of removal for jointing or terminating.The minimum thickness is 0.3mm and the maximum volume resistivity of 500 Ohm-m at 90°C. The screen is tightly fitted to the insulation to exclude all air voids and can be easily hand stripped on site.
Conducting Water Blocking Layer : The insulation screen may be coverd by semiconductive water blocking tape which will swell up under the influence of moisture of water to ensure longitudinal watertightness.
Metallic Layer : The metallic layer shall consist of either copper tapes or a concentric layer of copper wires or a combination of tapes and wires. The metallic layer provides an earth fault current path, capable of withstanding fault current to earth of 1000A for one second at maximum temperature 160°C. Copper wires are applied over the conducting water blocking layer with a minimum diameter of 0.5mm. As an alternative, copper tape(s) with minimum thickness of 0.1mm can be applied with overlap. Total cross section of copper wire screen and copper tape screen layer are shown in Table 2a and 2b.
Table 2a. Total Cross Section and Max. DC Resistance of Copper Wire Screen
Nominal Cross-Section of Cables | Total Cross Section | Max. DC Resistance of Copper Wire Screen at 20℃ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3.6/6KV (Um=7.2KV) | 6/10KV (Um=12KV) | 8.7/15KV (Um=17.5KV) | 12/20KV (Um=24KV) | 18/30KV (Um=36KV) | ||
mm² | mm² | Ω | ||||
70 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 1.19 |
95 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 1.19 |
120 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 1.19 |
150 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 0.759 |
185 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 0.759 |
240 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 0.759 |
300 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 0.759 |
400 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 0.271 |
500 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 0.217 |
630 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 0.271 |
Table 2b. Total Cross Section and Max. DC Resistance of Copper Tape Screen (0.1mm)
Nominal Cross-Section of Cables | Total Cross Section & Max. DC Resistance | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3.6/6KV (Um=7.2KV) | 6/10KV (Um=12KV) | 8.7/15KV (Um=17.5KV) | 12/20KV (Um=24KV) | 18/30KV (Um=36KV) | ||||||
Total Cross Section | Max. DC Resistance at 20℃ | Total Cross Section | Max. DC Resistance at 20℃ | Total Cross Section | Max. DC Resistance at 20℃ | Total Cross Section | Max. DC Resistance at 20℃ | Total Cross Section | Max. DC Resistance at 20℃ | |
mm² | mm² | Ω | mm² | Ω | mm² | Ω | mm² | Ω | mm² | Ω |
70 | 7.4 | 2.314 | 8.2 | 2.106 | 9.1 | 1.897 | 9.9 | 1.740 | 11.9 | 1.442 |
95 | 8.2 | 2.095 | 8.9 | 1.923 | 9.8 | 1.748 | 10.7 | 1.614 | 12.7 | 1.354 |
120 | 9.0 | 1.905 | 9.8 | 1.761 | 10.7 | 1.613 | 11.5 | 1.498 | 13.5 | 1.272 |
150 | 9.7 | 1.781 | 10.4 | 1.655 | 11.3 | 1.523 | 12.1 | 1.420 | 14.2 | 1.215 |
185 | 10.6 | 1.626 | 11.2 | 1.540 | 12.2 | 1.407 | 12.9 | 1.335 | 14.9 | 1.153 |
240 | 11.7 | 1.465 | 12.4 | 1.388 | 13.3 | 1.294 | 14.1 | 1.219 | 16.2 | 1.065 |
300 | 12.9 | 1.334 | 13.4 | 1.285 | 14.3 | 1.204 | 15.1 | 1.139 | 17.1 | 1.003 |
400 | 14.3 | 1.205 | 14.6 | 1.178 | 15.5 | 1.110 | 16.3 | 1.054 | 18.4 | 0.937 |
500 | 15.7 | 1.094 | 16.2 | 1.061 | 17.1 | 1.005 | 17.5 | 0.982 | 20.0 | 0.861 |
630 | 17.3 | 0.992 | 18.9 | 0.912 | 18.7 | 0.918 | 19.5 | 0.880 | 21.6 | 0.797 |
Separator / Water Blocking Layer : The metallic screen may be covered by non-conducting water blocking tape which will swell up under the influence of moisture of water to ensure longitudinal watertightness.
Separation Sheath (for armoured cable) : The separation sheath comprises a layer of extruded PVC, PE or LSZH, applied under the armour. Thickness of separation sheath as shown in table 3.
Table 3. Separation Sheath Thickness
Core Diameter | Approx.Thickess of Inner Sheath | |
|---|---|---|
mm | mm | |
> | < |
|
35 | 45 | 1.4 |
45 | 60 | 1.6 |
60 | 80 | 1.8 |
80 | - | 2.0 |
Armour (for armoured cable) : The armour consists of round aluminium wire armour applied helically over an extruded separation sheath.
Table 4. Round Armour Wire Diameter
Fictitious Diameter under the Armour | Armour Wire Diameter | |
|---|---|---|
mm | mm | |
> | < |
|
- | 10 | 0.8 |
10 | 15 | 1.25 |
15 | 25 | 1.6 |
25 | 35 | 2.0 |
35 | 60 | 2.5 |
60 | - | 3.15 |
The VDE 0276 Standard: A Benchmark for Quality and Safety
The VDE 0276 standard, developed by the German Association for Electrical, Electronic & Information Technologies (VDE), sets rigorous guidelines for power cables used in medium voltage applications. Specifically, Parts 620-622 of DIN VDE 0276, aligned with Harmonization Document (HD) 620 S1, govern the construction, testing, and performance of single core cables. This standard ensures that cables can withstand harsh conditions while maintaining high levels of electrical integrity and safety.
At its core, VDE 0276 emphasizes cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulation, which provides superior thermal and mechanical properties compared to traditional materials. The standard mandates water-blocking compounds to prevent moisture ingress, semi-conducting screens to eliminate air voids, and metallic layers for fault current protection. These features make the cables suitable for frequencies like 50 Hz, common in global power systems.
In the context of international compliance, VDE 0276 draws from IEC 60228 for conductor specifications and DIN VDE 0207 for insulation compounds. This harmonization ensures interoperability and reliability, making these single core cables a preferred choice in Europe and beyond. For industries in developing regions like South Africa, adhering to such standards mitigates risks associated with subpar infrastructure, such as cable failures during load shedding events that plague the country's grid.
Benefits: Why Choose VDE 0276 Single Core Cables?
The advantages of single core cables to VDE 0276 extend beyond compliance, offering tangible benefits for efficiency and longevity.
Durability and Reliability: XLPE insulation and water-blocking features make these cables resistant to environmental stressors like moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. This reduces downtime, critical in high-stakes sectors where power interruptions can cost millions.
Efficiency in Power Transmission: Low impedance and high capacitance values minimize energy losses, supporting efficient distribution over long distances. For aluminum conductors, lighter weight (e.g., 1750 kg/km vs. 3250 kg/km for copper in 240 mm² at 8.7/15 kV) lowers installation costs without compromising performance.
Safety Enhancements: Metallic screens handle fault currents effectively, preventing overheating or explosions. LSZH options reduce toxic emissions in fires, ideal for confined spaces like mines.
Cost-Effectiveness: Though initial costs may be higher, their long lifespan (often 40+ years) and low maintenance needs yield significant savings. In energy-scarce regions, they integrate seamlessly with renewables, extending grid-independent operations.
Environmental Impact: By enabling efficient power use and supporting green installations, these cables align with sustainability goals, such as reducing carbon footprints in heavy industries.
Usage Scenarios: From Global Applications to South Africa's Mining Challenges
Single core cables to VDE 0276 are versatile, suiting power stations, switchboards, and industrial setups. Indoors, they power machinery; outdoors, they handle underground or aerial distributions; in water, their watertight design excels.
In South Africa, the mining sector—contributing over 7% to GDP—faces acute power challenges. As of 2025, ongoing energy crises, including frequent load shedding and voltage instabilities, have disrupted operations, costing billions annually. According to recent reports from the South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy (SAIMM), power outages remain a top threat, prompting a shift toward resilient infrastructure and renewables.
Frequently Asked Questions
What voltages do single core cables to VDE 0276 support? They handle nominal Uo/U from 3.6/6 kV to 18/30 kV, with maximum operating voltages up to 36 kV.
Are these cables suitable for underground mining? Yes, their water-blocking and armored designs make them ideal for wet, subterranean installations.
How do they compare to multi-core cables? Single core variants offer easier handling in high-voltage scenarios and better heat dissipation in trefoil layouts.
What maintenance is required in harsh environments like South African mines? Annual inspections, thermography, and end-sealing to prevent moisture ingress.
Can they integrate with renewable energy sources? Absolutely, their efficiency supports solar or wind connections, crucial for off-grid mining operations.
What's the lifespan? Typically 30-50 years with proper installation, outlasting standard cables in demanding conditions.
Conclusion
Single core cables compliant with VDE 0276 represent a fusion of German engineering precision and practical innovation, essential for medium voltage power in today's industries. From their robust construction and superior specs to undeniable benefits like reliability and efficiency, they empower sectors facing energy hurdles. In South Africa, where mining grapples with power crises, these cables are proving indispensable for sustainable, resilient operations. As trends toward renewables accelerate, adopting such technologies will not only solve immediate challenges but pave the way for a greener industrial future. Whether you're an engineer, policymaker, or industry leader, understanding and implementing VDE 0276 cables could be the key to unlocking uninterrupted power.

Email Address: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
© 2025. All rights reserved.


One-click to Quickly Contact
Products
Contact
Company
Location:
Building A Private Science and Technology Park, Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone, Anhui Province, China
Heat Resistant Cable
WhatsApp: +86 17333223430
