Anhui Feichun Special Cable Co.,Ltd Email: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
Type A & B 1.1/1.1KV AS/NZS 1972/1125/3808
The Essential Role of Type A and B 1.1kV Cables in Ensuring Safety, Efficiency, and Compliance with AS/NZS 1972/1125/3808 Standards Amid South Africa's Mining Landscape
Type A & B 1.1/1.1KV AS/NZS 1972/1125/3808
Applications | These cables are used as 1.1kV cables to distribute power within the mine,suitable for use in underground coal mines. For Type A cables,optional 3 pilots can be selected. |
Standards | AS/NZS 1972:2006 |
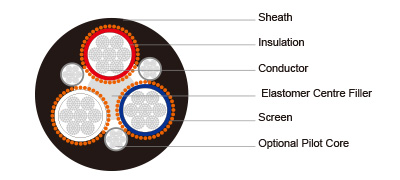
Construction 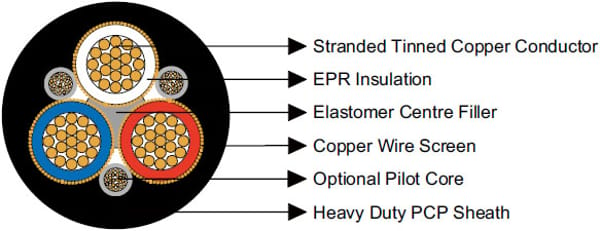 | |
Conductors | Stranded tinned annealed copper conductor. |
Insulation | EPR. |
Filling | Elastomer centre filler. |
Optional Pilot Core (Type A only) | CPE compositeinsulated and covered pilot conductor. |
Screen (earth conductor) | Copper wire. |
Sheath | Heavy duty PCP sheath. |
Dimensions and Weight
Nominal Conductor Area | Strand Size | Insulation Thickness | Core screen | Pilot Conductor | Nominal Sheath Thickness | Nominal Overall Diameter | Nominal Weight | ||
Strand Size | Area of Screen | Strand Size | Thickness of Covering | ||||||
mm² | No/mm | mm | mm | mm² | No/mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/100m |
Type A & B | |||||||||
16 | 7/1.70 | 1.4 | 48/0.40 | 6.0 | 24/0.20 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 24.6 | 120 |
25 | 19/1.35 | 1.4 | 57/0.40 | 7.2 | 32/0.20 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 28.0 | 170 |
35 | 19/1.53 | 1.5 | 63/0.40 | 7.9 | 30/0.25 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 30.4 | 205 |
50 | 19/1.78 | 1.7 | 72/0.40 | 9.0 | 50/0.25 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 34.9 | 270 |
70 | 19/2.14 | 1.8 | 67/0.50 | 13.2 | 80/0.25 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 40.2 | 370 |
95 | 19/2.52 | 2.0 | 77/0.50 | 15.1 | 80/0.25 | 2.0 | 3.8 | 46.1 | 490 |
120 | 37/2.03 | 2.2 | 65/0.67 | 22.9 | 80/0.25 | 2.0 | 3.8 | 51.1 | 615 |
150 | 37/2.25 | 2.3 | 70/0.67 | 24.7 | 80/0.25 | 2.0 | 4.4 | 56.0 | 740 |
185 | 37/2.52 | 2.5 | 78/0.67 | 27.5 | 80/0.25 | 2.0 | 5.1 | 62.3 | 915 |
240 | 61/2.25 | 2.7 | 45/1.35 | 64.4 | 80/0.25 | 2.0 | 5.7 | 72.9 | 1290 |
Understanding Cable Types: Type A and Type B 1.1kV Variants
At the heart of underground coal mining electrical systems are Type A and Type B cables, both rated for 1.1/1.1kV operations. These are not your everyday household wires; they are robust, purpose-built solutions compliant with Australian/New Zealand standards AS/NZS 1972:2006 for electric cables in underground coal mines, AS/NZS 1125 for conductors in insulated cables, and AS/NZS 3808 for insulating and sheathing materials.
Type A cables offer enhanced flexibility with an optional three-pilot core configuration. These pilots—composite insulated and covered with chlorinated polyethylene (CPE)—serve as monitoring conductors, allowing for real-time detection of faults, ground continuity checks, or integration with safety systems like methane detectors. This makes Type A ideal for scenarios requiring additional control or signaling alongside power transmission.
Type B, on the other hand, is a streamlined version without the optional pilots, focusing purely on power distribution. Both types share core features but cater to different operational needs: Type A for complex, monitored setups, and Type B for straightforward power delivery. Their design prioritizes safety in hazardous environments, where coal dust and gases pose explosion risks, adhering to flame-retardant and low-smoke properties outlined in the standards.
These cables are classified under low-voltage (LV) categories but are engineered for the rigors of mining, distinguishing them from general-purpose cables used in construction or utilities. In South Africa's context, where underground coal mines like those operated by companies such as Sasol or Exxaro dominate, the choice between Type A and B often hinges on the mine's automation level—trending upward as the industry embraces Industry 4.0 technologies.
Benefits: Why These Cables Outshine the Competition
The advantages of Type A and B cables extend beyond mere compliance. Their EPR insulation and PCP sheath provide exceptional resistance to mechanical damage, making them ideal for trailing applications where cables are dragged or flexed repeatedly. This durability translates to longer service life—often 10-15 years in harsh conditions—reducing downtime and replacement costs.
Safety is paramount: the tinned copper and screened design prevent arcing in methane-rich atmospheres, aligning with intrinsic safety protocols. Benefits include enhanced fault detection (via pilots in Type A), which can prevent accidents, and environmental resilience, crucial in South Africa's wet, acidic mine soils.
Economically, these cables support the mining industry's push toward efficiency. In a sector where energy costs can account for 30-40% of operations, their low-loss design optimizes power usage. Amid global trends like the mining cables market projected to grow from $12.64 billion in 2025, these cables enable scalability for electrified equipment, reducing reliance on diesel and cutting emissions—a key ESG factor.
Usage Scenarios: From Power Distribution to Advanced Applications
Primarily, these cables distribute 1.1kV power to pumps, conveyors, and lighting in underground coal mines. In a typical setup, a 95mm² Type B might power a longwall shearer, while Type A integrates with SCADA systems for remote monitoring.
In heavy industry, they extend to tunneling or quarrying. For South Africa, amid electrification trends, they're vital for battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) in mines, providing charging infrastructure without fossil fuels. Usage in hybrid solar setups, like Gold Fields' 50MW plant at South Deep, highlights their role in sustainable power delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What distinguishes Type A from Type B cables? Type A includes optional pilot cores for monitoring; Type B does not, making it simpler for basic power needs.
Are these cables suitable for non-mining applications? While optimized for mines, their robustness suits heavy industry like tunneling, but check standards for compliance.
How do they handle extreme temperatures? EPR insulation operates from -25°C to 90°C, with PCP sheath resisting up to 110°C short-term.
What's the impact of cable theft in SA mines? Theft disrupts power, costing billions; robust designs like these deter thieves and enhance security.
Can they integrate with smart mining tech? Yes, especially Type A, supporting IoT and automation for predictive maintenance.
How long do they last in underground conditions? 10-20 years with proper maintenance, far outlasting standard cables.
Type A and B 1.1kV cables, compliant with AS/NZS 1972/1125/3808, are more than wires—they're enablers of safe, sustainable mining. In South Africa, where trends like electrification and challenges like theft converge, these cables offer resilient solutions. As the industry evolves, embracing such technology will ensure mining remains a pillar of economic growth while prioritizing worker safety and environmental stewardship. Whether powering a shearer or stabilizing a pillar, they illuminate the path forward in the subterranean world.

Email Address: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
© 2025. All rights reserved.


One-click to Quickly Contact
Products
Contact
Company
Location:
Building A Private Science and Technology Park, Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone, Anhui Province, China
Heat Resistant Cable
WhatsApp: +86 17333223430
