Anhui Feichun Special Cable Co.,Ltd Email: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
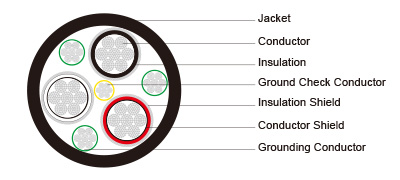
Type SHD-GC Three-Conductor Round Portable Power Cable, TPU Jacket 8kV to ICEA S-75-381
Type SHD-GC Three-Conductor Round Portable Power Cable with TPU Jacket: Engineered to Withstand the Harshest Environments While Ensuring Uninterrupted Power Supply
Type SHD-GC Three-Conductor Round Portable Power Cable, TPU Jacket 8kV to ICEA S-75-381
Applications | These heavy duty cables are designed for heavy mobile equipment such as drag lines, shovels, dredges, drills and for power feeders. |
Standards | ICEA S-75-381/NEMA WC 58 |
Construction 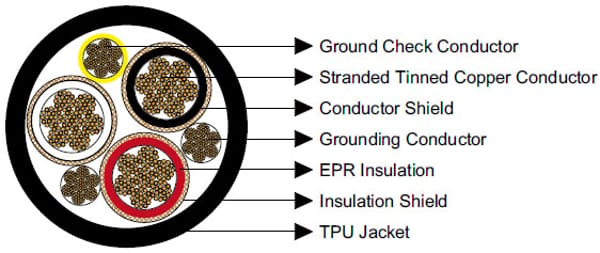 | |
Conductors | Stranded annealed tinned copper conductor. |
Conductor Shield | Semi-conducting layer. |
Insulation | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR). |
Insulation Shield | Conducting tape + Tinned copper/textile braid. |
Ground Check Conductor | Tinned copper with a yellow polypropylene insulation. |
Grounding Conductor | Tinned copper conductor. |
Jacket | Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) Jacket, black. |
Options | Other jacket materials such as CSP/PCP/NBR/PVC are available upon request. |
Mechanical and Thermal Properties | Minimum Bending Radius: 6×OD |
Dimensions and Weight:
Construction | No. of Strands | Grounding Conductor Size | Ground Check Conductor Size | Nominal Insulation Thickness | Nominal Jacket Thickness | Nominal Overall Diameter | Nominal Weight | Ampacity | ||||
No. of cores×AWG/kcmil | - | AWG/kcmil | AWG/kcmil | inch | mm | inch | mm | inch | mm | lbs/kft | kg/km | A |
3×4 | 259 | 8 | 8 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.205 | 5.2 | 1.94 | 49.3 | 2019 | 3004 | 122 |
3×2 | 259 | 6 | 8 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.220 | 5.6 | 2.12 | 53.8 | 2603 | 3873 | 159 |
3×1 | 259 | 5 | 8 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.220 | 5.6 | 2.21 | 56.1 | 2913 | 4334 | 184 |
3×1/0 | 266 | 4 | 8 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.220 | 5.6 | 2.32 | 58.9 | 3351 | 4986 | 211 |
3×2/0 | 323 | 3 | 8 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.235 | 6.0 | 2.46 | 62.5 | 3946 | 5871 | 243 |
3×3/0 | 418 | 2 | 8 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.250 | 6.4 | 2.62 | 66.5 | 4582 | 6817 | 279 |
3×4/0 | 532 | 1 | 8 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.250 | 6.4 | 2.75 | 69.8 | 5321 | 7917 | 321 |
3×250 | 627 | 1/0 | 6 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.250 | 6.4 | 2.89 | 73.4 | 6101 | 9077 | 355 |
3×350 | 888 | 2/0 | 6 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.280 | 7.1 | 3.21 | 81.3 | 7696 | 11450 | 435 |
3×500 | 1221 | 4/0 | 6 | 0.150 | 3.8 | 0.295 | 7.5 | 3.56 | 90.4 | 10199 | 15174 | 536 |
Benefits of Heavy-Duty Cables
Heavy-duty cables like Type SHD-GC offer several advantages:
Durability: The TPU jacket and robust construction resist abrasion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, ideal for harsh mining environments.
Flexibility: A minimum bending radius of 6×OD allows for easy installation in confined spaces.
Safety: Ground check and grounding conductors ensure fault detection and safe operation.
High Ampacity: Supports heavy machinery with high power demands, reducing the need for multiple cables.
Versatility: Suitable for applications like draglines, shovels, dredges, drills, and power feeders.
Usage Scenarios in South Africa’s Mining and Heavy Industry
South Africa’s mining sector, a cornerstone of the economy, relies heavily on robust power solutions. Heavy-duty cables like Type SHD-GC are integral to various applications:
Open-Pit Mining
In open-pit mines, such as those in the Northern Cape, draglines and shovels require flexible, high-ampacity cables to power massive electric motors. The Type SHD-GC’s TPU jacket withstands abrasive rock surfaces and extreme temperatures, while its ground check conductor ensures safety in high-voltage operations.
Underground Mining
In underground gold or platinum mines, such as those in Gauteng or Mpumalanga, cables power drills and ventilation systems. The cable’s flexibility and compact design make it ideal for confined spaces, while its EPR insulation protects against moisture and heat.
Heavy Industry
In industrial plants, such as steel manufacturing facilities in Mpumalanga, Type SHD-GC cables serve as power feeders for heavy machinery. Their high ampacity supports energy-intensive processes, and the TPU jacket resists chemical exposure from industrial processes.
es’ 243A ampacity (3×2/0 AWG) supported the mine’s draglines, boosting operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What makes Type SHD-GC cables suitable for mining?
A: Their TPU jacket, EPR insulation, and ground check conductor ensure durability, flexibility, and safety in harsh mining environments.
Q: Can these cables handle South Africa’s extreme temperatures?
A: Yes, they operate up to +90°C, suitable for the hot climates of mining regions like the Northern Cape.
Q: How often should cables be inspected?
A: Monthly inspections are recommended in high-stress environments like mines, with immediate repairs for any damage.
Q: Are alternative jacket materials necessary?
A: In corrosive environments, like chemical-heavy industrial plants, options like NBR or two-layer jackets enhance durability.
Q: What is the lifespan of Type SHD-GC cables?
A: With proper maintenance, they can last 5–10 years in demanding applications, depending on usage and environmental factors.
Heavy-duty cables like the Type SHD-GC are vital for powering South Africa’s mining and heavy industry sectors. Their robust construction, high ampacity, and safety features make them ideal for demanding applications, from open-pit draglines to industrial power feeders. By following proper installation and maintenance practices, businesses can maximize cable performance and longevity. As South Africa navigates challenges like load shedding and safety regulations, these cables offer reliable, efficient, and sustainable solutions, driving productivity in critical industries.

Email Address: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
© 2025. All rights reserved.


One-click to Quickly Contact
Products
Contact
Company
Location:
Building A Private Science and Technology Park, Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone, Anhui Province, China
Heat Resistant Cable
WhatsApp: +86 17333223430
