Anhui Feichun Special Cable Co.,Ltd Email: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
XLPE Insulated 6.35/11KV & 12.7/22KV High Voltage Cables AS/NZS 1972/1125/3808
XLPE Insulated High Voltage Cables: Unveiling the 6.35/11kV and 12.7/22kV Models for Demanding Industrial Applications in South Africa and Beyond
XLPE Insulated 6.35/11KV & 12.7/22KV AS/NZS 1972/1125/3808
Applications | These cables are used as HV feeder cables in fixed conditions. |
Standards | AS/NZS 1972:2006 |
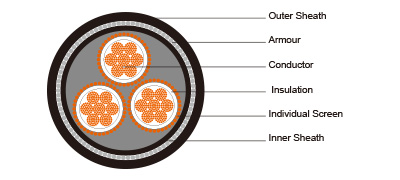
Construction 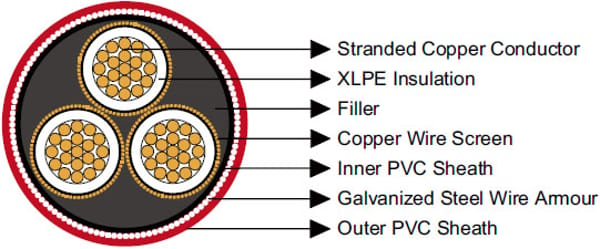 | |
Conductors | Stranded plain copper conductor. |
Insulation | XLPE. |
Individual Screen (earth conductor) | Copper wire. |
Inner Sheath | PVC sheath. |
Armour | Galvanized steel wire armour. |
Outer Sheath | PVC sheath to AS/NZS 1429.1. |
Dimensions and Weight
Nominal Conductor Area | Nominal Conductor Diameter | Insulation Thickness | Core screen | Armour Wire Diameter | Nominal Sheath Thickness | Nominal Overall Diameter | Nominal Weight | |
Strand Size | Area of Screen | |||||||
mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm² | mm | mm | mm | kg/100m |
6.35/11kV | ||||||||
16 | 4.8 | 3.4 | 10/0.85 | 5.7 | 2.00 | 2.4 | 46.6 | 330 |
25 | 5.8 | 3.4 | 10/0.85 | 5.7 | 2.50 | 2.5 | 50.1 | 415 |
35 | 6.8 | 3.4 | 11/0.85 | 6.2 | 2.50 | 2.6 | 52.8 | 475 |
50 | 8.0 | 3.4 | 15/0.85 | 8.5 | 2.50 | 2.7 | 55.7 | 540 |
70 | 9.6 | 3.4 | 21/0.85 | 11.9 | 2.50 | 2.8 | 59.6 | 645 |
95 | 11.5 | 3.4 | 29/0.85 | 16.5 | 2.50 | 2.9 | 63.9 | 775 |
120 | 13.1 | 3.4 | 36/0.85 | 20.4 | 2.50 | 3.1 | 67.9 | 905 |
150 | 14.5 | 3.4 | 44/0.85 | 25.0 | 2.50 | 3.2 | 71.5 | 1030 |
185 | 16.1 | 3.4 | 22/1.35 | 31.5 | 3.15 | 3.3 | 78.6 | 1280 |
240 | 18.5 | 3.4 | 29/1.35 | 41.5 | 3.15 | 3.5 | 84.7 | 1550 |
300 | 20.7 | 3.4 | 37/1.35 | 53.0 | 3.15 | 3.7 | 90.4 | 1820 |
400 | 23.6 | 3.4 | 47/1.35 | 67.3 | 3.15 | 4.0 | 97.9 | 2230 |
12.7/22kV | ||||||||
35 | 6.8 | 5.5 | 14/0.85 | 7.9 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 63.2 | 600 |
50 | 8.0 | 5.5 | 15/0.85 | 8.5 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 66.0 | 665 |
70 | 9.6 | 5.5 | 21/0.85 | 11.9 | 2.5 | 3.1 | 69.9 | 775 |
95 | 11.5 | 5.5 | 29/0.85 | 16.5 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 74.4 | 920 |
120 | 13.1 | 5.5 | 36/0.85 | 20.4 | 3.15 | 3.4 | 79.5 | 1140 |
150 | 14.5 | 5.5 | 44/0.85 | 25.0 | 3.15 | 3.5 | 83.1 | 1280 |
185 | 16.1 | 5.5 | 22/1.35 | 31.5 | 3.15 | 3.7 | 89.1 | 1450 |
240 | 18.5 | 5.5 | 29/1.35 | 41.5 | 3.15 | 3.9 | 95.0 | 1720 |
300 | 20.7 | 5.5 | 37/1.35 | 53.0 | 3.15 | 4.1 | 101.1 | 2010 |
400 | 23.6 | 5.5 | 47/1.35 | 67.3 | 3.15 | 4.3 | 108.2 | 2420 |
Benefits of XLPE Insulated HV Cables
XLPE insulated cables offer numerous advantages, making them a staple in modern power systems. Firstly, their high thermal resistance allows for greater current-carrying capacity compared to PVC-insulated cables, reducing energy losses and improving efficiency. This is particularly beneficial in energy-scarce environments like South Africa, where minimizing transmission losses can help alleviate load shedding impacts.
Mechanically, the galvanized steel wire armour protects against physical damage, abrasion, and rodents—common issues in mining tunnels or industrial sites. XLPE's moisture resistance prevents water treeing, a degradation phenomenon in older insulations, extending cable lifespan to 30-40 years or more with proper maintenance.
Environmentally, XLPE cables are halogen-free in some variants and recyclable, aligning with global sustainability trends. In heavy industry, they support higher voltage transmission with lower weight, easing logistics. Cost-wise, while initial investment is higher, reduced maintenance and downtime yield long-term savings. For instance, their flexibility simplifies installation in confined spaces, cutting labor costs. Overall, these benefits make XLPE cables indispensable for reliable, efficient power in demanding sectors.
Usage Scenarios
XLPE insulated HV cables excel in scenarios requiring stable power under stress. In mining, they serve as feeders for pumps, conveyors, and drilling equipment in underground operations, where armour withstands vibrations and debris. In heavy industry, like steel mills or chemical plants, they distribute power to high-load machinery.
Renewable integrations, such as solar farms connecting to grids, benefit from their efficiency. In urban utilities, they form backbone networks for substations. In South Africa, amid the energy transition, these cables facilitate microgrids in remote mines, reducing reliance on unstable national grids.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between 6.35/11kV and 12.7/22kV XLPE cables? The main difference lies in voltage rating and insulation thickness; 12.7/22kV has thicker insulation (5.5mm vs. 3.4mm) for higher voltages, suitable for longer distances or heavier loads.
Are these cables suitable for South African standards? Yes, while based on AS/NZS, they align with SANS 1507 for PVC/XLPE cables, widely used in SA mining.
How long do XLPE cables last? Typically 30-50 years, depending on installation and maintenance, with resistance to thermal aging.
Can they be used in wet environments? Absolutely; XLPE's moisture resistance and optional radial water blocking make them ideal for damp mining sites.
What are common failure modes? Partial discharges from poor joints or water treeing, preventable with regular testing.
Are they eco-friendly? Yes, lead-free and recyclable, supporting green initiatives in industry.
XLPE insulated 6.35/11kV and 12.7/22kV cables, with their robust design and AS/NZS compliance, offer a lifeline for power-reliant sectors. In South Africa, they address pressing energy challenges, fostering efficiency in mining and heavy industry. By adopting these technologies, industries can build resilient infrastructures for a sustainable future.

Email Address: Li.wang@feichuncables.com
© 2025. All rights reserved.


One-click to Quickly Contact
Products
Contact
Company
Location:
Building A Private Science and Technology Park, Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone, Anhui Province, China
Heat Resistant Cable
WhatsApp: +86 17333223430
